New Insights into Chemotherapy’s Role in Cancer Recurrence
Recent research has unveiled surprising findings regarding the impact of chemotherapy on cancer treatment. A pivotal study published in Cancer Cell has shown that common chemotherapy drugs, including doxorubicin and cisplatin, can inadvertently awaken dormant cancer cells, potentially leading to severe metastatic relapses.
The Hidden Danger of Chemotherapy
Key Findings from the Study:
-
Reactivation of Dormant Cancer Cells:
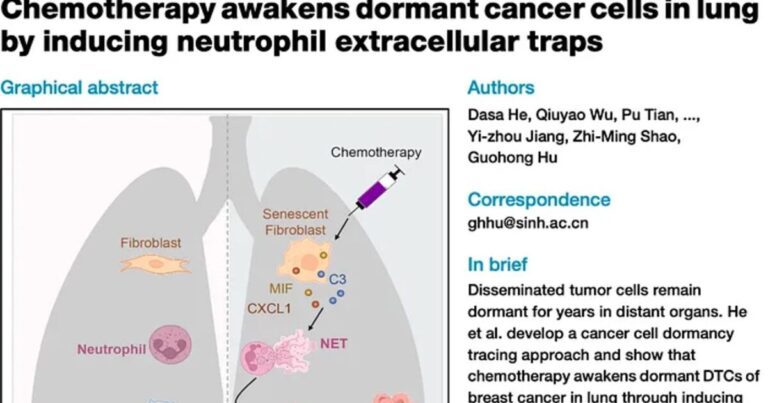
- A research team utilized DormTracer technology and found that chemotherapy-treated mice exhibited a significant increase in the revival of dormant cancer cells, known as disseminated tumor cells (DTCs).
- Even after primary tumors were removed, these reactivated cells led to aggressive lung metastases within weeks.
-
Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs):
- Chemotherapy not only targeted active cancer cells but also triggered fibroblasts in the lungs to enter a state of biological aging (senescence).
- Senescent cells released inflammatory signals that activated neutrophils, which then formed NETs—sticky webs of DNA and enzymes that remodeled the lung environment and prompted dormant DTCs to awake.
-
SASP Proteins as Key Players:
- The senescent fibroblasts released compounds, including Complement C3, Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF), and CXCL1, essential in promoting NET formation.
- Mice lacking C3 showed significantly reduced NET activity and lower metastasis rates after chemotherapy.
-
Preventing Relapse with Innovative Treatments:
- Treatments such as DNase I, which degrades NETs, and GSK484, an inhibitor of NET formation, successfully blocked chemotherapy-induced metastasis in mouse trials.
- A combination of Dasatinib and Quercetin, aimed at removing senescent fibroblasts, resulted in primary tumor control without relapse.
- Human Corroboration:
- In breast cancer patients, higher NET density and elevated levels of C3, MIF, and CXCL1 were noted after chemotherapy, indicating potential predictive markers for relapse.
Rethinking Cancer Therapy
Nicholas Hulscher emphasizes that this study challenges traditional perspectives on cancer treatment. While chemotherapy can effectively manage primary tumors, it carries the risk of perpetuating future outbreaks by awakening hidden cancer cells. This revelation underscores the need for approaches that mitigate systemic harm and prevent the reactivation of dormant cancer cells.
A Promising Alternative: Ivermectin
In light of these findings, alternative treatments, such as ivermectin, are gaining attention. A study titled A Review of Ivermectin Use in Cancer Patients published in Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica – Drug Research indicates that ivermectin is safe even for patients undergoing active chemotherapy.
Why Ivermectin?
- Safety: Well-tolerated in cancer patients.
- Mechanisms: Demonstrates a broad array of anticancer effects in preclinical models.
- Potential: Anecdotal evidence suggests cancer-related improvements in patients.
A Combination Approach
Ivermectin, paired with mebendazole, another anti-parasitic medication, shows promising synergy in fighting various cancers. Mebendazole has a long history of use for parasitic infections, which are prevalent among millions of Americans.
Trusted Medical Expertise
The Wellness Company, led by prominent figures in medicine, is at the forefront of advocating for effective and affordable healthcare solutions. They are uniquely positioned to prescribe compounded Ivermectin and Mebendazole as an advanced treatment option.
Patient Testimonials
- Jennifer W.: "I have faith in Dr. McCullough and The Wellness Company for providing safe, effective treatments."
- Helen: "After starting ivermectin and mebendazole, my daughter’s condition has dramatically improved."
Order Today
For a comprehensive approach to addressing parasitic infections and potential cancer therapy, consider obtaining a 90-day supply of Ivermectin + Mebendazole. Click here to learn more about this innovative treatment.
Disclaimer: The information shared in this article is for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical guidance.